- Rotary printing
- Digital printing
- Screen printing
- Pad printing
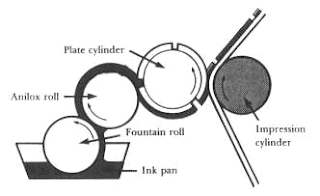
A printing process where the printing plates are wrapped around a cylinder.
Offset lithography
Etched aluminium plates are wrapped around a cylinder and transfer ink to an offset rubber blanket roller and then onto the print surface.
Retrogravure
Copper plates print straight onto the print surface, plates are more durable so better for long print runs.
Flexography
Uses a positive mirror image flexible relief plate. Can be used for printing almost any type of substrate including plastic, metallic films, cellophane and paper. Transfers 'sticky' ink, normally low quality so used for disposable print such as food packaging.
Digital printing
Suited for short run print jobs, able to print on a range of medias from paper to metal. Has a higher cost than traditional offset printing methods, but usually cheaper in the long run by the saving of the making of the printing plates.
Screen printing
A woven mesh to support an ink blocking stencil. It is more versatile than more traditional printing methods, the surface does not have to be printed under pressure unlike lithography. Different inks can be used to work with a variety of different materials such as textiles, ceramics , wood, paper, glass and metal.
Pad printing
A printing process that allows you to transfer a 2-D image onto a 3-D object.
Design for print usually falls under four categories:
Branding and identity
Brand - The perceived emotional corporate image as a whole.
Identity - The visual aspects that form part of the overall brand.
Logo - A logo identifies a business in its simplest form via the use of a mark or icon.
Packaging and promotion
Packaging is the science, art, and technology of enclosing or protecting products for distribution, storage, sale, and use.
Packaging contains, protects, preserves, transports, informs, and sells.
Packaging also refers to the process of design, evaluation, and production of packages.
Promotion is the communication link between sellers and buyers for the purpose of influencing, informing, or persuading a potential buyer's purchasing decision.
(Boxes on shelves, things we wear, things we hold while using something, point of sale units, banners, floor graphics,& more….)
Publishing and editorial
Publishing is the process of production and dissemination of literature or information—the activity of making information available to the general public.
Traditionally, the term refers to the distribution of printed works such as books and newspapers but design
publishing includes the stages of the development, acquisition, copyediting, graphic design, production (printing) of
Magazines, Novels, Coffee table books, Manuals, Reference books etc.
Info graphics and wayfinding
Information graphics (infographics) are graphic visual representations of information, data or knowledge. These infographics present complex or unfamiliar information quickly and clearly. (Harry Beck-Underground Tube map is a good example)
Traffic signs and other public signs rely heavily on information graphics, such as stylised human figures, icons and emblems to represent concepts such as yield, caution, and the direction of traffic. Public places such as transit terminals usually have some sort of integrated "signage system" with standardised icons and stylised maps.
Technical manuals and instructions make extensive use of diagrams and infographics. Newspapers often use infographics to describe something that is either complex or unfamiliar. A visual example might be how many London busses high is Mount Everest.





No comments:
Post a Comment